Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) – Liquefied Natural Gas: A Reliable Methane Solution
In summary, Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is natural gas cooled to its liquid state (below -161°C or -258°F), reducing its volume by approximately 600 times, making it more economical and safer to store and transport when there are no pipelines.
Liquefied Natural Gas – Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) is natural gas that has been cryogenically cooled into a liquid state, below the methane boiling point of -161°C or -258°F.
It’s the same gas that powers stoves, heaters, and numerous other applications in homes and businesses around the world.
Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) is primarily composed of methane and is naturally produced.
At ELGAS, we focus on unlocking the potential of stranded gas—small, isolated gas deposits that aren’t economically viable for traditional pipelines.
Our specialization lies in micro-LNG plants that transform these stranded resources into valuable energy sources.
By leveraging cutting-edge technology developed by our parent company, Linde, we make it possible to utilize stranded gas for high-volume industrial and commercial applications.
This technology offers compelling benefits as a fuel source, including: providing cost-effective energy solutions for a wide range of applications.
Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) is a cleaner-burning fuel compared to other fossil fuels, helping reduce greenhouse gas emissions and supporting sustainable energy practices.
Image courtesy of Linde

LNG Meaning
LNG is the acronym that stands for liquefied natural gas, which is natural gas that has been cooled to a liquid state, below -161°C or -258°F, making storage and transport easier and more cost effective.
Why Natural Gas is Liquefied
The liquification process reduces the volume of the natural gas by more than 600 times, making storage and transport more feasible and economical to locations without a pipeline.
This makes long distance transport possible, including transoceanic shipments by LNG ships.
LNG allows the supply of natural gas to areas that are not served by natural gas pipelines.
Summary of How LNG Works
- Raw natural gas is cleaned of impurities, any water is removed, natural gas liquids are stripped out, and then it is processed by an LNG plant.
- Dry natural gas (methane) is cooled to its liquid state, below the methane boiling point of -161°C or -258°F.
- The liquefied natural gas (LNG) can then be stored in cryogenic tanks or transported in special cryogenic trucks or ships.
- At the point of use, the LNG is warmed to convert it back into a gas, called regasification, and then used on site or distributed through a pipeline.
Regasification of LNG
At the point of use, the LNG is warmed to transform it back to its gaseous state, using an LNG vaporizer.
This process is called regasification.
Then the LNG is either used on site or transported by pipeline to distribution companies, industrial consumers, and power plants.
Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) Explained

Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) , or Liquefied Natural Gas, is simply natural gas (methane) in a liquid form.
Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) is natural gas cooled cryogenically to below its boiling point of −161°C.
This changes the natural gas from its gaseous state to a liquid, reducing its volume by 600:1 (1m³ of LNG = 600m³ of methane gas).
To use Liquid Natural Gas (LNG), it goes through a regasification process, transforming from a liquid back to a gas.
Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) is used just as you would pipeline natural gas.
Put simply, Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) is Natural Gas Made Portable™.
Liquid Natural Gas (LNG), which is predominantly Methane, is an odourless, non-toxic and non-corrosive.
If spilled, the Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) evaporates quickly and disperses, leaving no residue.
Benefits of Liquid Natural Gas (LNG)
- Reduced storage volume of natural gas of more than 600 times as LNG goes from its gaseous state to liquid.
- The volume reduction allows it to be transported more efficiently over long distances.
- Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) can be supplied to locations without a pipeline, including remote destinations.
- Small LNG plants can be used to process “stranded natural gas” in gas fields to small to justify a pipeline.
Advantages of Liquid Natural Gas (LNG)
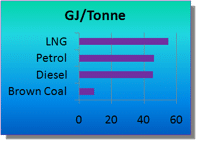
LNG GJ/Tonne
Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) is a locally supplied Australian resource which does not rely on imports. This increases supply reliability and provides flexibility for growth.
- Unlike the price of diesel which is linked to the ever-volatile oil market, the price of Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) is much more stable, which allows for more control in business budgeting.
- Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) can be transported over 1,000KM efficiently from its source of supply.
- The energy content of Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) ranges from 24 MJ/L to 21 MJ/L or 52-55 MJ/Kg.
- The energy density of Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) is roughly 0.41 kg/L to 0.5 kg/L, depending mostly on temperature and pressure.
- The energy density of Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) is 2.4 times greater than CNG.
- Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) is stored in vertical tanks and reduces the required space for large energy or large volume fuel source requirements.
LNG Trade
- LNG is used domestically, in Australia, for larger industrial customers without pipeline access.
- LNG is also being used as a transport fuel for large reticulated trucks.
- LNG is traded internationally, with Australia being one of the largest LNG exporters.
Liquefied Natural Gas Price – LNG Price
The liquefied natural gas price (LNG price) in Australia is influenced by LNG exports.
LNG exports drive up the price of natural gas for both LNG exports and domestic pipeline natural gas use.
However, the same isn’t always true if the natural gas comes from stranded natural gas fields.
As stranded natural gas would be difficult to export, the export demand doesn’t affect it.
The liquefied natural gas price (LNG price) from stranded natural gas reserves tends to be more stable and is frequently offered on multi-year contracts.
In addition, for larger commercial users, the liquefied natural gas price (LNG price) is frequently less than that for LPG, providing some incentive to switch from LPG to LNG.

Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) for Electricity Generation
Liquid Natural Gas (LNG), in its natural gas form, can be used to power stationary energy installations ranging from internal combustion to microturbine to industrial scale gas turbine generation.
Modular & Scalable Micro Gas Turbine Electricity Generation
For the SME market, there are a range of stationary Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) electricity generation solutions.
Gas microturbine generation modules can have individual ratings of 200 kW to 250 kW and are fully scalable.
So, as your company and electricity needs grow, you can simply add more microturbine modules.
Image courtesy of Capstone Turbine Corp.
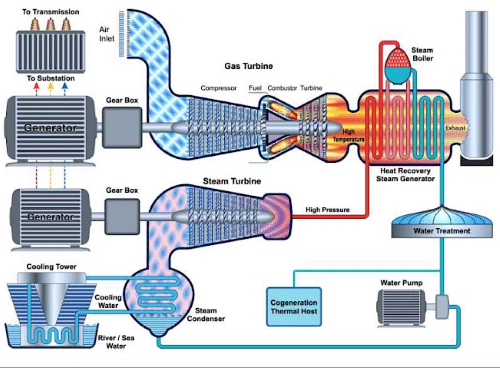
Combined Cycle Gas Turbine – CCGT
One of the most energy efficient Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) designs is that of the combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT).
These units take the waste heat from the gas turbine and capture it in the form of steam, which is typically used to power steam turbine generators.
They generate steam with a heat recovery steam generator (HRSG).
Overall efficiency of a Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) stationary installation is approximately 60%.
Image courtesy of Ipieca Ltd.
Other Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) Applications
Mining and Industrial

Mining and industrial markets have considerable potential employ Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) into their operations.
Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) is currently used in power generation, boilers, fluid bed dryers, rotary kilns and furnaces.
Large quantities of diesel are consumed by mining vehicles.
These vehicles are typically used only on a particular site with short repetitive routes.
This makes them ideal for refuelling at a one site location.
Gas Fired Boilers

Industrial and commercial boilers are one of the most common uses for Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) in Australia.
The industries include dairy products, manufacturing, food processing and construction products.
Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) fired boilers burn much cleaner than oil fired boilers.
LNG Powered Ferries & Buses

Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) is a great fuel to power transport on fixed routes.
Ferries typically have multiple gas engine generator sets giving power to electric driven thrusters.
Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) tanks are usually sized to take full truck loads of Liquid Natural Gas (LNG).
Committed to a Sustainable Future
ELGAS is committed to working with our customers, industry and government as we transition to a decarbonised Net Zero economy by 2050.
 As one of Australia’s largest suppliers of Industrial gases, we understand our responsibility to find renewable alternatives to fossil fuel energy sources while reducing our emissions and the emissions of our customers at the same time.
As one of Australia’s largest suppliers of Industrial gases, we understand our responsibility to find renewable alternatives to fossil fuel energy sources while reducing our emissions and the emissions of our customers at the same time.
There is no environmental cleanup needed for Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) spills on water or land.
- Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) has no particulate emissions
- No ground or water contamination
- Improved air quality
- Reduced CO2 emissions vs traditional fuels
